Photovoltaic Effect
"What Is ?" > What Is Electric Energy ? > Energy Conversion
The Photovoltaic (PV) Effect refers to the physical and chemical phenomena which result in an electric potential across some materials when light hits them. This effect was discovered in 1839 by the French physicist A.E. Becquerel (1820-1891). About 1% of all electric energy generation in the USA is based on this effect.
Most of the recent solar plant development in the USA is based on the Photovoltaic Effect. Some solar developments are more conventional as they use the sun to provide heat to create steam that then is used to turn turbines that drive the rotors of electrical generators based on Faraday's Law of induction. An example is the Ivanpah Solar Power Facility in San Bernardino County, California.
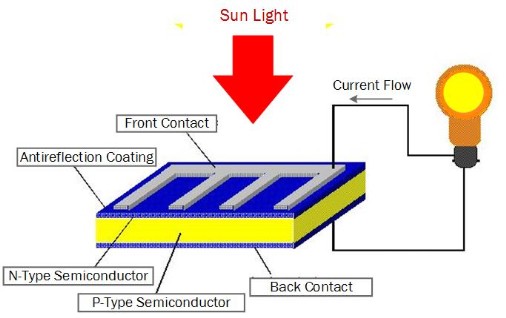
Electricity Generation Based on the Photovoltaic Effect
Recent developments use Solar Panels made of arrays of photovoltaic cells. As illustrated above, a typical cell is is made with N-Type and P-Type silicon wafers arranged as shown above. When the sun shines on the cell, an electrical potential develops across the front and back contacts. This potential causes a current to flows in a wire connected between the contacts.